Question 972631: 1. The absolute value of "a" is (never, sometimes, always) equal to "a".
2. The absolute value of "x" is (never, sometimes, always) equal to "-x".
3. The absolute value of ""y" is (never, sometimes, always) equal to a positive integer.
4. "x" is (never, sometimes,always)greater than "x".
5. Can you show the steps in the solutions to these problems?
Thank you.
Answer by MathLover1(20850)   (Show Source): (Show Source):
You can put this solution on YOUR website!
1. The absolute value of " " is (never, sometimes, always) equal to " " is (never, sometimes, always) equal to " ". ".
The absolute value of  , denoted " , denoted " " is the distance of " is the distance of  from zero. This is why absolute value is from zero. This is why absolute value is 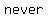  ; absolute value only asks " ; absolute value only asks "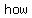 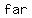 ?", not " ?", not "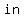 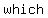 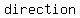 ?" ?"
so, your answer is:
The absolute value of " " is " is 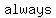 equal to " equal to " " "
2. The absolute value of " " is (never, sometimes, always) equal to " " is (never, sometimes, always) equal to " ". ".
since, by definition, absolute value is 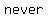  , your answer is: , your answer is:
The absolute value of " " is " is 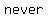 equal to " equal to " ". ".
3. The absolute value of " " is (never, sometimes, always) equal to a positive integer. " is (never, sometimes, always) equal to a positive integer.
The absolute value of an integer is the numerical value without regard to whether the sign is negative or positive.  could be an integer, or decimal... could be an integer, or decimal...
The absolute value of " " is " is 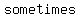 equal to a positive integer. equal to a positive integer.
4. " " is " is 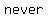 greater than " greater than " ". ".
5. Can you show the steps in the solutions to these problems?
steps shown above
|
|
|