Question 885741: a body at rest attains a velocity V after free falling through distance h. Calculate the further distance the body is to travel to attain velocity 2V.
Answer by KMST(5328)   (Show Source): (Show Source):
You can put this solution on YOUR website! You can learn physics, write/juggle formulas, and/or apply calculus, but the answer is simple and easy once you find it.
When starting from rest, and under constant acceleration,
final velocity is proportional to time,  , ,
and distance is proportional to time squared  . .
To double the velocity requires to double the time, and that quadruples the total distance traveled.
To speed up to double the velocity, 2V , it will take 2t.
As time increases by a factor of  , ,
distance (proportional to  ) increases by a factor of ) increases by a factor of  . .
While going from 0 to 2V, the distance traveled is 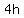 , ,
so the body travels  further. further.
JUGGLING FORMULAS:
Starting from rest, and at a constant acceleration,  , ,
the velocity after a time  will be will be  , ,
and the distance traveled will be  times the average velocity times the average velocity  . .
So,  . .
Also, since  <---> <---> , ,
 --> --> gives you the relation of final velocity attained to total distance traveled. gives you the relation of final velocity attained to total distance traveled.
If final velocity is 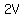 and the additional distance is and the additional distance is  , ,
the total distance is
 ---> ---> ---> ---> ---> ---> ---> ---> ---> ---> . .
|
|
|