Question 852051: an isosceles right angled triangle has one side length of (x+2) cm and the length of the hypotenuse is 12 cm. Find the perimeter
Answer by KMST(5328)   (Show Source): (Show Source):
You can put this solution on YOUR website! I cannot decide if this is a trick geometry question, or an attempt at mixing algebra and geometry.
With the length of the hypotenuse, the isosceles right triangle is uniquely determined, so we do not need any other length.
The variable  shows up, unneeded, adding nothing but confusion. shows up, unneeded, adding nothing but confusion.
The problem says that the length of one side is   , but does not ask to find , but does not ask to find  . If we tried to find . If we tried to find  , since the problem does not specify if the side measuring , since the problem does not specify if the side measuring   is one leg of the triangle or the hypotenuse, we would find two possible values for is one leg of the triangle or the hypotenuse, we would find two possible values for  , but it would still be the same triangle, with the same perimeter. , but it would still be the same triangle, with the same perimeter.
AS A TRICK PROBLEM TO BE SOLVED THE SMART WAY:
An isosceles right angled triangle has two equally long sides, called legs, opposite 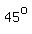 angles. angles.
If we call the length of the hypotenuse  , the Pythagorean theorem tells has that the length of each leg will be , the Pythagorean theorem tells has that the length of each leg will be 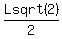 because because
 --> --> --> --> --> -->
Then, the perimeter is

So if the hypotenuse measures 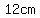 , ,
the perimeter is 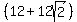  . .
PRETENDING THAT THIS IS AN ALGEBRA PROBLEM,
and that they meant that the side with a length of (x+2) cm is not the hypotenuse.
If the length of one of the legs of the right isosceles triangle is  cm, cm,
the length of the other leg of the right isosceles triangle is also  cm. cm.
Then, the Pythagorean theorem says that





That is the length (in cm) of each leg of the isosceles right triangle, and that is all we need, because we have not been asked to find the value of  . .
Then, the perimeter (in cm) would be
 . .
|
|
|