The basic graph of y = sin(x) has these 5 major points,
zero,max,zero,min,zero, which are:
(0,0), (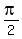 ,1),
,1), 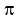 ,0), (
,0), (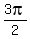 ,1), (
,1), ( ,0)
Your graph has the corresponding 5 major points, starting
with the point nearest the origin:
(
,0)
Your graph has the corresponding 5 major points, starting
with the point nearest the origin:
(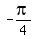 ,0), (
,0), ( ,-3),
,-3),  ,0), (
,0), ( ,1), (
,1), ( ,0)
The period is
,0)
The period is  since the last x value of the five is
since the last x value of the five is  , and
the first of the five is
, and
the first of the five is 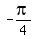 , so they have difference
, so they have difference
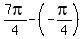 =
=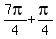 =
=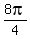 =
= ,
same as the basic sine graph,
,
same as the basic sine graph, 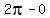 =
= so there is no horizontal
stretching or shrinking.
Each of the 5 major x-coordinates of your graph is pi/4 less than its
corresponding x-coordinate on the basic sine graph:
so there is no horizontal
stretching or shrinking.
Each of the 5 major x-coordinates of your graph is pi/4 less than its
corresponding x-coordinate on the basic sine graph:
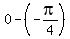 =
=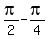 =
=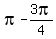 =
=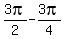 =
= =
= So the horizontal shift, commonly called the phase shift, is
So the horizontal shift, commonly called the phase shift, is  units to the
left. Therefore the equation of your graph will have (x-
units to the
left. Therefore the equation of your graph will have (x-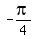 ) or
) or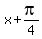 substituted
for x.
Each of the 5 major y-coordinates of the basic sine graph are 0,1,0,-1,0,
whereas the 5 corresponding major y-coordinates of your graph are 0,-3,0,3,0,
They are all multiplied by -3. The negative sign reflects the graph in the
x-axis and the 3 stretches it by a factor of 3 vertically. Therefore the right
side of the equation of your graph will have a factor of -3. So the equation
of your graph is found by starting with the basic sine graph:
y = sin(x)
Then replace the x by
substituted
for x.
Each of the 5 major y-coordinates of the basic sine graph are 0,1,0,-1,0,
whereas the 5 corresponding major y-coordinates of your graph are 0,-3,0,3,0,
They are all multiplied by -3. The negative sign reflects the graph in the
x-axis and the 3 stretches it by a factor of 3 vertically. Therefore the right
side of the equation of your graph will have a factor of -3. So the equation
of your graph is found by starting with the basic sine graph:
y = sin(x)
Then replace the x by 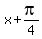 and multiply the right side by -3, and get
y = -3sin
and multiply the right side by -3, and get
y = -3sin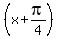 .
Edwin
.
Edwin