y²-4y-6x+13 = 0
Since y is squared the standard (vertex) form is
(y-k)² = 4p(x-h) (Some books use "a" instead of "p")
The vertex is the point (h,k)
The parabola will open right if the sign of p turns
out to be positive and it will open left if it turns
out to be negative.
y²-4y-6x+13 = 0
Isolate the terms in y on the left side of the equation:
y²-4y = 6x-13
Complete the square on the left:
1. Multiply the coefficient of y by  .
. 



 2. Square the result of step 1.
2. Square the result of step 1. 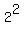

 3. Add the result of step 2 to both sides of the equation.
y²-4y+4 = 6x-13+4
1. Factor the trinomial on the left as a perfect square.
(y-2)(y-2) = (y-2)²
2. Combine the numbers on the right side of the equation:
(y-2)² = 6x-9
Factor the coefficient of x out on the right side. This will
involve a fraction since we have to factor 6 out of -9. Had
it been -12, it would have been easy but we have no choice
but to factor 6 out of -9 and get a fraction
3. Add the result of step 2 to both sides of the equation.
y²-4y+4 = 6x-13+4
1. Factor the trinomial on the left as a perfect square.
(y-2)(y-2) = (y-2)²
2. Combine the numbers on the right side of the equation:
(y-2)² = 6x-9
Factor the coefficient of x out on the right side. This will
involve a fraction since we have to factor 6 out of -9. Had
it been -12, it would have been easy but we have no choice
but to factor 6 out of -9 and get a fraction 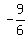 which is
what we get when we divide -9 by 6. Then
which is
what we get when we divide -9 by 6. Then 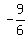 reduces to
reduces to 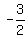 .
So the standard form is:
(y-2)² = 6(x-
.
So the standard form is:
(y-2)² = 6(x- )
We compare that to:
(y-k)² = 4p(x-h)
and see that k=2 and h=
)
We compare that to:
(y-k)² = 4p(x-h)
and see that k=2 and h= and 4p=6 or p=
and 4p=6 or p= =
= Therefore the vertex is (h,k) = (
Therefore the vertex is (h,k) = ( ,2) and since
p is a positive number the parabola will open to the right.
So we plot the vertex:
,2) and since
p is a positive number the parabola will open to the right.
So we plot the vertex:
 Since p=
Since p= or
or  and the parabola opens to the right
the focus is
and the parabola opens to the right
the focus is  units to the right of the vertex. A parabola
always curves around its focus, and since the parabola opens right,
that's how we know that the focus is to the right of the vertex. The
focus will have the same y-coordinate as the vertex, but its x-coordinate
will be
units to the right of the vertex. A parabola
always curves around its focus, and since the parabola opens right,
that's how we know that the focus is to the right of the vertex. The
focus will have the same y-coordinate as the vertex, but its x-coordinate
will be  or
or  units to the right of the vertex
(
units to the right of the vertex
( ,2), and since
,2), and since 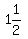 = 3, the focus will be
the point (3,2). We plot the focus:
= 3, the focus will be
the point (3,2). We plot the focus:
 The directrix will be a vertical line p=
The directrix will be a vertical line p= units left of the
vertex, which will mean that the directrix will coincide with the
y-axis. So the y-axis IS the directrix and its equation is x=0.
To sketch the parabola we draw the focal chord (the so-called "latus rectum")
which has length 4p = 6 units with the focus at its midpoint:
units left of the
vertex, which will mean that the directrix will coincide with the
y-axis. So the y-axis IS the directrix and its equation is x=0.
To sketch the parabola we draw the focal chord (the so-called "latus rectum")
which has length 4p = 6 units with the focus at its midpoint:
 Now we can sketch in the parabola:
Now we can sketch in the parabola:
 Summary. The standard form equation is (y-2)² = 6(x-
Summary. The standard form equation is (y-2)² = 6(x- )
The parabola opens right
The vertex is (
)
The parabola opens right
The vertex is ( ,2)
The focus is (3,2)
The directrix is the line whose equation is x=0 which
happens to be the y-axis.
The focal chord, focal width, or latus rectum is 6 units
and extends from the point (3,-1) to (3,5)
The axis of symmetry is the line through the vertex and focus
which bisects the parabola. It is the dotted line and its
equation is y=2.
That's more information that what you asked for, but you may need
to give that on other parabola problems.
Edwin
,2)
The focus is (3,2)
The directrix is the line whose equation is x=0 which
happens to be the y-axis.
The focal chord, focal width, or latus rectum is 6 units
and extends from the point (3,-1) to (3,5)
The axis of symmetry is the line through the vertex and focus
which bisects the parabola. It is the dotted line and its
equation is y=2.
That's more information that what you asked for, but you may need
to give that on other parabola problems.
Edwin