Question 798185: A 5 foot long pole leans against a wall. The bottom is 3 feet from the wall. How much farther should the bottom be pulled away from the wall so that the top moves the same amount down the wall?
Answer by KMST(5328)   (Show Source): (Show Source):
You can put this solution on YOUR website! THE MENTAL MATH SOLUTION:
 because (3,4,5) (with because (3,4,5) (with  ) is the most famous Pythagorean triple. ) is the most famous Pythagorean triple.
(It is the only one I can remember and a favorite of math teachers).
A Pythagorean triple is a set of 3 natural numbers (positive integers) that could be the measures of the sides of a right triangle, because the squares of the first two numbers add up to the square of the third number.
A 5 meter pole leaning against a wall, with the bottom at 3 meters from the wall has its top 4 meters high on the wall.
 
A 5 meter pole leaning against a wall, with the bottom at 4 meters from the wall has its top 3 meters high on the wall.
 It's a flipped version of the same right triangle. It's a flipped version of the same right triangle.
THE INTENDED SOLUTION:
Of course it is harder, as you should expect from a math teacher.
We find that the pole reaches a height of  meters up the wall when its bottom is 3 meters from the wall by using the Pythagorean theorem. meters up the wall when its bottom is 3 meters from the wall by using the Pythagorean theorem.
 --> --> --> --> --> --> --> -->
As the base of the right triangle is increased by a distance  (in meters), from (in meters), from  to to  , the height is decreased by a distance , the height is decreased by a distance  (in meters), from (in meters), from  to to 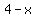 . .
According to the Pythagorean theorem:





The solution  --> --> means not moving the pole at all, and is not what the problem requires. means not moving the pole at all, and is not what the problem requires.
The other solution,  --> --> means moving the bottom of the pole 1 meter away from the wall, so it will be 4 meters from the wall, which will get the top to reach 3 meters up the wall. means moving the bottom of the pole 1 meter away from the wall, so it will be 4 meters from the wall, which will get the top to reach 3 meters up the wall.
|
|
|