It's complete enough to know what you mean.
H0
μ = 40
H1
μ < 40
If the mean really is 40 with the standard deviation of 12.5
then we find the probability that 38.7 would be that low or
lower, and if it's less than 5% of the time, it's too unlikely
and we'll reject the null hypothesis, but if it's not we won't.
Calculate the z-score:
x - m 38.7 - 40
————— = ————————— = -.7353910524
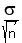
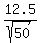 1. The first way you have to know the cut off points for the
various alpha error values.
In the case of a left one-tail test with alpha = 0.05 you have to
have the cut-off point of -1.64, for that's the value that has 0.05
of the area to the left of it.
2. The second way you find the p-value, which is the area to the
left of the z-score -.735 which is 0.2312, which is higher than
0.05.
When the p-value is high, the null must fly.
When p-value is low, the null must go
Here the p-value is high, so the null must fly, so we fail to reject
the null hypothesis.
Edwin
1. The first way you have to know the cut off points for the
various alpha error values.
In the case of a left one-tail test with alpha = 0.05 you have to
have the cut-off point of -1.64, for that's the value that has 0.05
of the area to the left of it.
2. The second way you find the p-value, which is the area to the
left of the z-score -.735 which is 0.2312, which is higher than
0.05.
When the p-value is high, the null must fly.
When p-value is low, the null must go
Here the p-value is high, so the null must fly, so we fail to reject
the null hypothesis.
Edwin