Question 762417: What are the basis postulates of the geometry?
Found 2 solutions by solver91311, MathLover1:
Answer by solver91311(24713)   (Show Source): (Show Source):
You can put this solution on YOUR website!
Read the first chapter of your Geometry book.
John

Egw to Beta kai to Sigma
My calculator said it, I believe it, that settles it
Answer by MathLover1(20850)   (Show Source): (Show Source):
You can put this solution on YOUR website!
Postulates are statements that are assumed to be true without proof. Postulates serve two purposes - to explain undefined terms, and to serve as a starting point for proving other statements.
  : :
Point-Line-Plane Postulate
A) Unique Line Assumption: Through any two points, there is exactly one line.
Note: This doesn't apply to nodes or dots.
B) Dimension Assumption: Given a line in a plane, there exists a point in the plane not on that line. Given a plane in space, there exists a line or a point in space not on that plane.
C) Number Line Assumption: Every line is a set of points that can be put into a one-to-one correspondence with real numbers, with any point on it corresponding to zero and any other point corresponding to one.
Note: This doesn't apply to nodes or dots. This was once called the Ruler Postulate.
D) Distance Assumption: On a number line, there is a unique distance between two points.
E) If two points lie on a plane, the line containing them also lies on the plane.
F) Through three noncolinear points, there is exactly one plane.
G) If two different planes have a point in common, then their intersection is a line.
Euclid's Postulates
A) Two points determine a line segment.
B) A line segment can be extended indefinitely along a line.
C) A circle can be drawn with a center and any radius.
D) All right angles are congruent.
Note: This part has been proven as a theorem. See below, proof.
E) If two lines are cut by a transversal, and the interior angles on the same side of the transversal have a total measure of less than 180 degrees, then the lines will intersect on that side of the transversal.
Polygon Inequality Postulates
Triangle Inequality Postulate: The sum of the lengths of two sides of any triangle is greater than the length of the third side.
Quadrilateral Inequality Postulate: The sum of the lengths of 3 sides of any quadrilateral is greater than the length of the fourth side.
  : :
Postulates of Equality
Reflexive Property of Equality: 
Symmetric Property of Equality: if  , then , then 
Transitive Property of Equality: if  and and  , then , then 
.
Postulates of Equality and Operations
Addition Property of Equality: if  , then , then 
Multiplication Property of Equality: if  , then , then 
Substitution Property of Equality: if  , then , then  can be substituted for can be substituted for  in any equation or inequality in any equation or inequality
Subtraction Property of Equality: if  , then , then 
Postulates of Inequality and Operations
Addition Property of Inequality: if 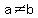 , then , then 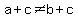
Multiplication Property of Inequality: if 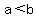 and and  , then , then 
if 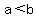 and and  , then , then 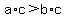
Equation to Inequality Property: if a and b are positive, and  , then , then 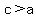 and and 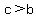
if a and b are negative, and  , then , then 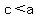 and and 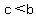
Subtraction Property of Inequality: if 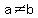 , then , then 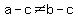
Transitive Property of Inequality: if 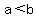 and and 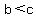 , then , then 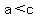
Postulates of Operation
Commutative Property of Addition:
Commutative Property of Multiplication: 
Distributive Property:  and vv and vv
|
|
|