y < 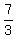 x - 5
First we draw the graph of the boundary line y =
x - 5
First we draw the graph of the boundary line y = 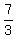 x - 5.
Two points on that line are (0,-5) and (3,2). We must draw the line
dotted because the inequality is < and therefore does not include
the boundary line:
x - 5.
Two points on that line are (0,-5) and (3,2). We must draw the line
dotted because the inequality is < and therefore does not include
the boundary line:
 Since the line does not go through the origin we can use (0,0) as
a test point to see whether the origin is a solution. If it is a
solution then all points are on the same side of the boundary line
as the origin and if the origin is not a solution, all the solutions
are on the side the origin is not on. So we substitute (x,y) = (0,0)
in the original inequality:
y <
Since the line does not go through the origin we can use (0,0) as
a test point to see whether the origin is a solution. If it is a
solution then all points are on the same side of the boundary line
as the origin and if the origin is not a solution, all the solutions
are on the side the origin is not on. So we substitute (x,y) = (0,0)
in the original inequality:
y < 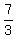 x - 5
0 <
x - 5
0 < 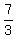 ·0 - 5
0 < -5
That is false so we must shade the side of the line that the origin
is not on:
·0 - 5
0 < -5
That is false so we must shade the side of the line that the origin
is not on:
 Edwin
Edwin