
First let  . This is the matrix formed by the coefficients of the given system of equations. . This is the matrix formed by the coefficients of the given system of equations.
Take note that the right hand values of the system are  , ,  , and , and  and they are highlighted here: and they are highlighted here:

These values are important as they will be used to replace the columns of the matrix A.
Now let's calculate the the determinant of the matrix A to get  . To save space, I'm not showing the calculations for the determinant. However, if you need help with calculating the determinant of the matrix A, check out this solver. . To save space, I'm not showing the calculations for the determinant. However, if you need help with calculating the determinant of the matrix A, check out this solver.
Notation note:  denotes the determinant of the matrix A. denotes the determinant of the matrix A.
---------------------------------------------------------
Now replace the first column of A (that corresponds to the variable 'x') with the values that form the right hand side of the system of equations. We will denote this new matrix 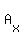 (since we're replacing the 'x' column so to speak). (since we're replacing the 'x' column so to speak).

Now compute the determinant of 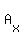 to get to get  . Again, as a space saver, I didn't include the calculations of the determinant. Check out this solver to see how to find this determinant. . Again, as a space saver, I didn't include the calculations of the determinant. Check out this solver to see how to find this determinant.
To find the first solution, simply divide the determinant of 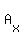 by the determinant of by the determinant of 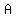 to get: to get: 
So the first solution is 
---------------------------------------------------------
We'll follow the same basic idea to find the other two solutions. Let's reset by letting  again (this is the coefficient matrix). again (this is the coefficient matrix).
Now replace the second column of A (that corresponds to the variable 'y') with the values that form the right hand side of the system of equations. We will denote this new matrix  (since we're replacing the 'y' column in a way). (since we're replacing the 'y' column in a way).

Now compute the determinant of  to get to get  . .
To find the second solution, divide the determinant of  by the determinant of by the determinant of 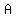 to get: to get: 
So the second solution is 
---------------------------------------------------------
Let's reset again by letting  which is the coefficient matrix. which is the coefficient matrix.
Replace the third column of A (that corresponds to the variable 'z') with the values that form the right hand side of the system of equations. We will denote this new matrix 

Now compute the determinant of  to get to get  . .
To find the third solution, divide the determinant of  by the determinant of by the determinant of 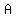 to get: to get: 
So the third solution is 
====================================================================================
Final Answer:
So the three solutions are  , ,  , and , and  giving the ordered triple (3, 2, -1) giving the ordered triple (3, 2, -1)
Note: there is a lot of work that is hidden in finding the determinants. Take a look at this 3x3 Determinant Solver to see how to get each determinant.
|