Question 458709: Use the Rational Root Theorem to list all possible rational roots for each equation. Then find any actual roots.
x^3+2x^2+3x+6=0
Answer by robertb(5830)   (Show Source): (Show Source):
You can put this solution on YOUR website! Applying the rational root theorem, possible rational roots are -6, -3,-2, -1, 1,2,3,6.
Using the remainder theorem (or synthetic division), trying out x = -2:
 Hence x = -2 is a rational root. After synthetic division, the quotient is Hence x = -2 is a rational root. After synthetic division, the quotient is 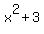 , which doesn't even have real roots. , which doesn't even have real roots.
|
|
|