Here is the sample space. It contains 36 possible outcomes:
(1,1) (1,2) (1,3) (1,4) (1,5) (1,6)
(2,1) (2,2) (2,3) (2,4) (2,5) (2,6)
(3,1) (3,2) (3,3) (3,4) (3,5) (3,6)
(4,1) (4,2) (4,3) (4,4) (4,5) (4,6)
(5,1) (5,2) (5,3) (5,4) (5,5) (5,6)
(6,1) (6,2) (6,3) (6,4) (6,5) (6,6)
Now I will color the ones red which have a sum of at least 5:
(1,1) (1,2) (1,3) (1,4) (1,5) (1,6)
(2,1) (2,2) (2,3) (2,4) (2,5) (2,6)
(3,1) (3,2) (3,3) (3,4) (3,5) (3,6)
(4,1) (4,2) (4,3) (4,4) (4,5) (4,6)
(5,1) (5,2) (5,3) (5,4) (5,5) (5,6)
(6,1) (6,2) (6,3) (6,4) (6,5) (6,6)
Count the red ones. There are 30 of them. (it's easier to count the
6 non-red ones and subtract from 36 to get 30).
So the probability of a sum of at least 5 is 30 out of 36, which gives
us the fraction 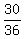 which reduces to
which reduces to  .
Edwin
.
Edwin