Quadratic equation  (in our case (in our case  ) has the following solutons: ) has the following solutons:

For these solutions to exist, the discriminant  should not be a negative number. should not be a negative number.
First, we need to compute the discriminant  : :  . .
Discriminant d=17 is greater than zero. That means that there are two solutions:  . .


Quadratic expression 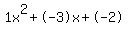 can be factored: can be factored:

Again, the answer is: 3.56155281280883, -0.56155281280883.
Here's your graph:
 |