Question 172054: find the additive inverse of each number: -4+6i.
find the absolute value of each complex number: 6i
solve each quadratic equation: -x^2+5x-2=0, x^2-8x+7=0
i know the first two are pretty simple, i'm just not sure exactly how to do them.
and the last two i am completely confused on them :(
Answer by solver91311(24713)   (Show Source): (Show Source):
You can put this solution on YOUR website! The additive inverse of any number is that number when added to the original number results in a sum of zero. So if  is your original number, the additive inverse is is your original number, the additive inverse is  because because  for all for all  . .
To sum two complex numbers, add the real parts and add the imaginary parts, thus:

So, in order to find the additive inverse of 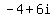 we need to determine the additive inverses of both we need to determine the additive inverses of both  and and  , namely , namely  and and 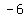 . Hence the additive inverse of . Hence the additive inverse of 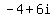 is is 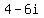 because because

******************************
The absolute value of a complex number  is given by is given by  . .
In this case, you are looking for 
******************************
 are the two roots of a quadratic equation of the form are the two roots of a quadratic equation of the form 
All you need to do is plug in the values of the coefficients in your quadratic equation and do the arithmetic. Remember to use a factor of i if the part under the radical is less than zero.
For your first equation,  , ,  , and , and  , so: , so:



Hence  and and 
These are the exact representations of the two roots of this quadratic. If you want numerical approximations, use your calculator. Seek guidance from your text or your instructor as to the required precision whenever numerical approximations are required.
**********************************
The other problem is worked exactly the same way, and again has a positive discriminant, the second one also has real number roots.
|
|
|