|
Question 132453: Discuss completely (as in the textbook) and draw the graphs of the following rational functions.

Found 2 solutions by jim_thompson5910, edjones:
Answer by jim_thompson5910(35256)   (Show Source): (Show Source):
You can put this solution on YOUR website! I'm not sure as to what you mean by "Discuss completely (as in the textbook)", but I'm assuming that you want to find the asymptotes right?
 Start with the given function Start with the given function
Looking at the numerator 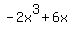 , we can see that the degree is , we can see that the degree is  since the highest exponent of the numerator is since the highest exponent of the numerator is  . For the denominator . For the denominator  , we can see that the degree is , we can see that the degree is  since the highest exponent of the denominator is since the highest exponent of the denominator is  . .
Oblique Asymptote:
Since the degree of the numerator (which is  ) is greater than the degree of the denominator (which is ) is greater than the degree of the denominator (which is  ), there is no horizontal asymptote. In this case, there's an oblique asymptote ), there is no horizontal asymptote. In this case, there's an oblique asymptote
To find the oblique asymptote, simply use polynomial division to find it. The quotient of 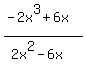 is the equation of the oblique asymptote is the equation of the oblique asymptote
___-x__________-_3___
2x^2-6x | -2x^3 + 0x^2 + 6x
-2x^3 + 6x^2
----------
-6x^2 + 6x
-6x^2 + 18x
-------------
-12x
note: in this case, we don't need to worry about the remainder
Since the quotient is 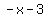 , this means that the oblique asymptote is , this means that the oblique asymptote is 
--------------------------------------------------
Vertical Asymptote:
 Start with the given function Start with the given function
 Factor out the GCF Factor out the GCF
 Cancel like terms Cancel like terms
So we're left with
 where where  (this is where a hole occurs) (this is where a hole occurs)
To find the vertical asymptote, just set the denominator equal to zero and solve for x
 Set the denominator equal to zero Set the denominator equal to zero
 Add 3 to both sides Add 3 to both sides
 Combine like terms on the right side Combine like terms on the right side
So the vertical asymptote is 
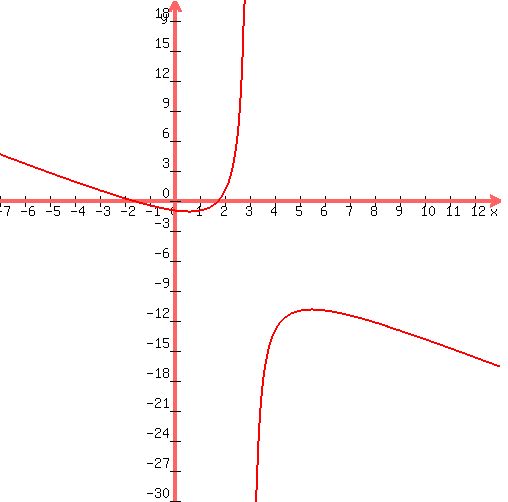
Notice if we graph  , we can visually verify our answers: , we can visually verify our answers:
 Graph of Graph of  with the oblique asymptote with the oblique asymptote  (blue line) and the vertical asymptote (blue line) and the vertical asymptote  (green line) and the hole (green line) and the hole  (the small circle drawn) (the small circle drawn)
Answer by edjones(8007)   (Show Source): (Show Source):
You can put this solution on YOUR website! 
when x=3 then the denominator=0
So, 3 is the vertical asymptote.
The domain is all real numbers except x=3 and x=0
Since the numerator is 1 degree larger than the denominator there is no horizontal asymptote but a slant asymptote.
It is -x-3 found by doing long division on the numerator by the denominator.
The almost vertical line is an artifact and not an asymptote.
.
Ed
|
|
|
| |