|
Question 131924This question is from textbook structure and method
: Please help!
How do you know if a value is a solution for an inequality?
How is this different from determining if a value is a solution to an equation? If you replace the equal sign of an equation with an inequality sign, is there ever a time when the same value will be
a solution to both the equation and the inequality? Write an inequality and provide a value that
may or may not be a solution to the inequality.
Please and Thank You=)
This question is from textbook structure and method
Found 2 solutions by solver91311, barbara.roberts:
Answer by solver91311(24713)   (Show Source): (Show Source):
You can put this solution on YOUR website! How do you know if a value is a solution for an inequality?
Answer: Substitute the value for the variable and do whatever arithmetic is necessary to see if you have a true statement or not. If the statement is true, the value is an element of the solution set. If the statement is false, it is not an element of the solution set.
How is this different from determining if a value is a solution to an equation?
Answer: The method is not different.
If you replace the equal sign of an equation with an inequality sign, is there ever a time when the same value will be a solution to both the equation and the inequality?
Answer: Yes, but only if the inequality sign is the "or equal" variety. For example, given the equation  , replace the equal sign with a 'greater than or equal' sign: , replace the equal sign with a 'greater than or equal' sign:  . In this case, 5 is an element of the solution set for both the equation and the inequality. However, given the same equation and replacing the equal sign with a 'greater than' sign results in this inequality: . In this case, 5 is an element of the solution set for both the equation and the inequality. However, given the same equation and replacing the equal sign with a 'greater than' sign results in this inequality: 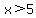 . In this case, the equation and the inequality have no elements of their solution sets in common. There is only one element in the solution set to the equation, namely the number 5. There are an infinite number of elements in the solution set to the inequality, but none of those elements are the number 5. . In this case, the equation and the inequality have no elements of their solution sets in common. There is only one element in the solution set to the equation, namely the number 5. There are an infinite number of elements in the solution set to the inequality, but none of those elements are the number 5.
Write an inequality and provide a value that may or may not be a solution to the inequality.
Answer: 
4 is not an element of the solution set
2 is an element of the solution set
Answer by barbara.roberts(1)   (Show Source): (Show Source):
You can put this solution on YOUR website! ubstitute the value for the variable and do whatever arithmetic is necessary to see if you have a true statement or not. If the statement is true, the value is an element of the solution set. If the statement is false, it is not an element of the solution set.
How is this different from determining if a value is a solution to an equation?
Answer: The method is not different.
If you replace the equal sign of an equation with an inequality sign, is there ever a time when the same value will be a solution to both the equation and the inequality?
Answer: Yes, but only if the inequality sign is the "or equal" variety. For example, given the equation x=5, replace the equal sign with a 'greater than or equal' sign: x>=5. In this case, 5 is an element of the solution set for both the equation and the inequality. However, given the same equation and replacing the equal sign with a 'greater than' sign results in this inequality: x>5. In this case, the equation and the inequality have no elements of their solution sets in common. There is only one element in the solution set to the equation, namely the number 5. There are an infinite number of elements in the solution set to the inequality, but none of those elements are the number 5.
Write an inequality and provide a value that may or may not be a solution to the inequality.
Answer: x<=3
4 is not an element of the solution set
2 is an element of the solution set
|
|
|
| |