.
A car is initially stationary. It has a constant acceleration of 2.0 ms^-2.
a. Calculate the velocity of the car after 10 seconds .
b. Calculate the distance travelled by the car at the end of 10 seconds .
c. Calculate the time taken by the car to reach a velocity of 24 ms^-1.
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
The general formula for the velocity is v = at for the given situation
(uniform acceleration at the zero initial speed).
Here "a" is the given acceleration; t is the time from the start, and v is the current speed.
(a) Using this formula, you get for (a) v = 2 m/s^2 * 10 seconds = 20 m/s.
For the traveled distance, the formula is d = 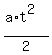 =
= 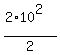 =
= 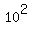 = 100 meters.
It is the answer for question (b).
To answer (c), you need to find t from this simple linear equation
v = at, or 24 = 12*t,
from which you have t =
= 100 meters.
It is the answer for question (b).
To answer (c), you need to find t from this simple linear equation
v = at, or 24 = 12*t,
from which you have t =  = 12 seconds.
= 12 seconds.
Solved and answered, with all necessary explanations.