Question 1168931: Find the (standard) equation of the hyperbola whose foci are 𝐹1(-3,0) and 𝐹2(3,0),
such that for any point on it, the absolute value of the difference of its distances
from the foci is 3.
Found 2 solutions by MathLover1, ikleyn:
Answer by MathLover1(20850)   (Show Source): (Show Source):
You can put this solution on YOUR website!
given:
foci are F1( , , ) and F2( ) and F2( , , ), ),
such that for any point on it, the absolute value of the difference of its distances from the foci is 
The standard form of a hyperbola with a horizontal transverse axis is

where ( , , ) is the center of the hyperbola ) is the center of the hyperbola
 is the distance from the center to a vertex is the distance from the center to a vertex
 is the distance from the center to a co-vertex is the distance from the center to a co-vertex
The center of the hyperbola is the midpoint of the line segment between the foci, which is


so, the center of the hyperbola is at ( , , ) )
The distance between the foci is 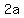 , so , so  => =>
The distance from each focus to the center is 
.
using  find find 



So, the equation of the hyperbola is:

since  , this is , this is  a valid hyperbola a valid hyperbola
The foci and vertices coincide, so the hyperbola degenerates into a line.
The hyperbola with the given parameters doesn't exist.
Answer by ikleyn(52856)   (Show Source): (Show Source):
You can put this solution on YOUR website! .
Find the (standard) equation of the hyperbola whose foci are 𝐹1(-3,0) and 𝐹2(3,0),
such that for any point on it, the absolute value of the difference of its distances from the foci is 3.
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
The solution by @MathLover1 is INCORRECT.
I came to bring a correct solution.
Since the foci are F1(-3,0) and F2(3,0), we conclude that
- the major axis is horizontal y= 0 and coincides with x-axis;
- the center is at (0,0), half way between the foci;
- the distance between the foci is 3 - (-3) = 6 units and the distance
from the center to the foci c = 6/2 = 3 units.
So, the general equation of the hyperbola is
 - -  = 1,
where a > 0 is the horizontal transfer semi-axis.
Now consider this condition "for any point on it, the absolute value of the difference of its distances from the foci is 3.".
We know that 'a' is the distance along x-axis from the center (0,0) to any of the two vertices of the hyperbola.
Then the points (-a,0) and (a,0) are the points on this hyperbola.
For point (a,0), the distance from F1 is (3-a); the distance from F2 is (a+3).
The difference of these distance must be 3, according to the condition.
So, we write this equation
(a+3) - (3-a) = 3,
2a = 3,
a = 3/2 = 1.5.
So, the vetices are at (-1.5,0) and (1.5,0), and 'a', as we found, is 1.5.
Then from equation a^2 + b^2 = c^2 we can find 'b^2'
1.5^2 + b^2 = 3^2
b^2 = 3^2 - 1.5^2 = 9 - 2.25 = 6.75.
Hence, the standard equation of this hyperbola is = 1,
where a > 0 is the horizontal transfer semi-axis.
Now consider this condition "for any point on it, the absolute value of the difference of its distances from the foci is 3.".
We know that 'a' is the distance along x-axis from the center (0,0) to any of the two vertices of the hyperbola.
Then the points (-a,0) and (a,0) are the points on this hyperbola.
For point (a,0), the distance from F1 is (3-a); the distance from F2 is (a+3).
The difference of these distance must be 3, according to the condition.
So, we write this equation
(a+3) - (3-a) = 3,
2a = 3,
a = 3/2 = 1.5.
So, the vetices are at (-1.5,0) and (1.5,0), and 'a', as we found, is 1.5.
Then from equation a^2 + b^2 = c^2 we can find 'b^2'
1.5^2 + b^2 = 3^2
b^2 = 3^2 - 1.5^2 = 9 - 2.25 = 6.75.
Hence, the standard equation of this hyperbola is
 - - 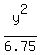 = 1. <<<---=== ANSWER = 1. <<<---=== ANSWER
Solved correctly.
|
|
|