.
The term "the collision is perfectly elastic" means that after the collision the masses remain the same
and both the momentum law and conservation of mechanical energy law are held.
If 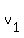 and
and 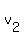 are the velocities of the particles after the collision, then the momentum conservation equation is
2 kg * 1 m/s + 1 kg * 0 m/s =
are the velocities of the particles after the collision, then the momentum conservation equation is
2 kg * 1 m/s + 1 kg * 0 m/s =  +
+  ,
Left side is the momentum value BEFORE the collision; right side is that AFTER the collision. In the short form
,
Left side is the momentum value BEFORE the collision; right side is that AFTER the collision. In the short form
 +
+ 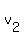 = 2 (kilogram*meter/s). (1)
The mechanical energy conservation equation is
= 2 (kilogram*meter/s). (1)
The mechanical energy conservation equation is
 +
+  =
=  +
+  .
Left side is the kinetic energy value BEFORE the collision; right side is that AFTER the collision. In the short form
.
Left side is the kinetic energy value BEFORE the collision; right side is that AFTER the collision. In the short form
 +
+  = 1 (kg*m^2/s^2, or joules). (2)
Thus you need solve the system of two equation (1) and (2) to find the unknowns
= 1 (kg*m^2/s^2, or joules). (2)
Thus you need solve the system of two equation (1) and (2) to find the unknowns 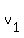 and
and 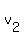 .
For it, from equation (1), express
.
For it, from equation (1), express 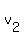 and substitute it into equation (2).
In this way, you can complete the solution on your own.
and substitute it into equation (2).
In this way, you can complete the solution on your own.