.
The sum of an infinite geometric progression converges if and only if the common ratio is less than 1 by the modulus. In your case it means
|2n -1| < 1, or, equivalently,
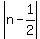 <
<  .
The solution to the last inequality are all those "n" that are remoted less than
.
The solution to the last inequality are all those "n" that are remoted less than  from
from  , i.e.
0 < n < 1.
Or, in the interval notation, those "n" that belong to the interval (0,1) (the ends are not included !).
, i.e.
0 < n < 1.
Or, in the interval notation, those "n" that belong to the interval (0,1) (the ends are not included !).
Solved.