Question 1090305: use the p over q method and synthetic division to factor the polynomial P(x). then solve P(x)=0
P(x)=x^3+4x^2+x-6
Found 2 solutions by Boreal, MathLover1:
Answer by Boreal(15235)   (Show Source): (Show Source):
You can put this solution on YOUR website! P(x)=x^3+4x^2+x-6
p is 6 and q is 1, the coefficient of x^3
therefore the possible integer roots are +/-1,2,3,6
synthetic division with
1/1----4----1---minus 6
==1==5----6----0
1 is a root, so (x-1) is a factor
the other factor may be read off the division as x^2+5x+6, which is (x+3)(x+2)
Those are the three factors, and roots are -3, -2, and 1

Answer by MathLover1(20850)   (Show Source): (Show Source):
You can put this solution on YOUR website! P(x)=x^3+4x^2+x-6
1. Arrange the polynomial in descending order:

2. Write down all the factors of the constant term. These are all the possible values of p .
 , all the factors are , all the factors are
 = =  ,± ,±  , , , ,
3. Write down all the factors of the leading coefficient. These are all the possible values of q .

4.Write down all the possible values of  . Remember that since factors can be negative, . Remember that since factors can be negative, 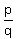 and and 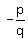 must both be included. Simplify each value and cross out any duplicates. must both be included. Simplify each value and cross out any duplicates.
 =± =± , ± , ±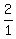 ,± ,±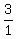 , ± , ± ,... (eliminate ,... (eliminate  , it is product of , it is product of 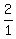 and and 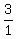 ) )
 =± =± , ± , ± ,± ,± , ,
5. Use synthetic division to determine the values of 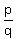 for which for which  . These are all the rational roots of . These are all the rational roots of 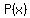 . .
The synthetic division table is: if 
 |.... |....  .... ....  .... .. .... .. .... .... 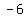
................... .... .. .... .. .... .. .... ..
-----------------------------------------
......... ........ ........ ....... ....... ........ ........ -> reminder=> -> reminder=>  ,=> ,=>  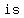 a root a root
The synthetic division table is: if 
 |.... |....  .... ....  .... .. .... .. .... .... 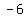
................... .... ....  .... .... .... ....
-----------------------------------------
......... ........ ........ ...... ...... .... .... -> reminder -> reminder  => =>  is is  root root
The synthetic division table is: if 
 |.... |....  .... ....  .... .. .... .. .... .... 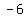
................... .... .. .... .. .... ....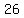
-----------------------------------------
......... ........ ........ ....... ....... ........ ........ -> reminder=> -> reminder=>  ,=> ,=>  is is  a root a root
The synthetic division table is: if 
 |.... |....  .... ....  .... .. .... ..  .... .... 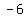
...................  .... .. .... ..  .... .... 
-----------------------------------------
.........  ........ ........  ....... .......  ....... .......  -> reminder=> -> reminder=>  ,=> ,=>  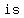 a root a root
The synthetic division table is: if 
 |.... |....  .... ....  .... .. .... ..  .... .... 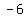
...................  .... .. .... ..  .... .... 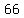
-----------------------------------------
.........  ........ ........  ....... .......  ........ ........  -> reminder=> -> reminder=>  ,=> ,=>  is is  a root a root
The synthetic division table is: if 
 |.... |....  .... ....  .... .. .... .. .... .... 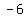
................... .... .. .... .. .... .... 
-----------------------------------------
......... ........ ........ ....... ....... ........ ........ -> reminder=> -> reminder=>  ,=> ,=>  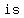 a root a root

then solve

if  => =>
if  => =>
if  => =>
|
|
|