I will change your numbers and do this one instead,
which is step by step exactly like yours.
So you can use it as a model to do yours by.
Graph the equation below using the three listed methods.
y= -3x + 6
Methods:
table of values
slope intercept form
X and Y intercepts
Explain each step as you graph the equation
-------------------------
table of values:
x | y | (x,y)
----------------
1 | |
2 | |
3 | |
4 | |
I arbitrarily chose 1,2,3,and 4 for x and substituted them into
the given equation:
y = -3x + 6 y = -3x + 6 y = -3x + 6 y = -3x + 6
y = -3(1) + 6 y = -3(2) + 6 y = -3(3) + 6 y = -3(4)+6
y = -3+6 y = -6 + 6 y = -9 + 6 y = -12 + 6
y = 3 y = 0 y = -3 y = -6
Then I finished filling in the table:
x | y | (x,y)
----------------
1 | 3 | (1,3)
2 | 0 | (2,0)
3 | -3 | (3,-3)
4 | -6 | (4,-6)


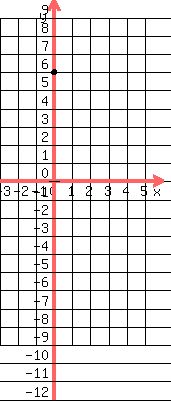
 That's the first way.
------------------------------------
That's the first way.
------------------------------------
Slope-intercept form methof:
Compare the equation y = -3x + 6
to the equation y = mx + b
and you see that m = -3 and b = 6
m = -3 is the slope and b is the y-intercept.
Always consider the slope m as a fraction. In this case m = -3
is not a fraction, so we put a 1 under it to make it into a
fraction, because slope is the fraction 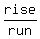 . The fraction
we use for the slope is
. The fraction
we use for the slope is 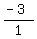 .
The numerator is the "rise". The denominator is the "run".
.
The numerator is the "rise". The denominator is the "run".






 --------------------------------------------
--------------------------------------------
X and Y intercept method:
To find the x-intercept, the point where the line crosses the
x-axis, substitute 0 for the other letter, y, and solve for x.
y = -3x + 6
0 = -3x + 6
3x = 6
x = 2, so the line crosses the x-axis at 2.
To find the y-intercept, the point where the line crosses the
y-axis, substitute 0 for the other letter, x, and solve for y.
y = -3x + 6
y = -3(0) + 6
y = 0+6
y = 6, so the line crosses the y-axis at 6.
[Notice that this is the same y-intercept that we used in the
previous method].



 Now, do your equation exactly the same way in every detail,
step by step.
Edwin
Now, do your equation exactly the same way in every detail,
step by step.
Edwin