Question 1069954: 1 3 5 are the first three terms of the first differences of a quadratic sequence. The 7th term of the quadratic sequence is 35.
1.determine the 6th and 5th terms of the quadratic sequence (4)
2.Determine the nth term of the quadratic sequence(5)
Answer by KMST(5328)   (Show Source): (Show Source):
You can put this solution on YOUR website! DISCLAIMERS:
1) Different teachers/schools/countries use
different symbols/formulas/names. For a few examples, what in USA is usually called arithmetic sequence is an arithmetic progression, or an AP in other places, and "trapezoid" and "billion" also change meaning as you move from one place to another.
2) Your teacher may have given you formulas and "recipes" to solve
"problems of this type" , and may even have a certain preferred or required homework format. I cook from scratch, and solve problems the same way, without using memorized formulas or procedures, only remembering formulas that I have used too often, and seem obvious to me from the most basic definitions.
(MY) SYMBOL DEFINITIONS:
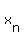 = term number = term number  in the quadratic sequence. in the quadratic sequence.
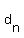 = first-difference number = first-difference number  in the quadratic sequence, so that in the quadratic sequence, so that

FOR THIS SEQUENCE
 tells us that the second-difference is tells us that the second-difference is
 throughout the sequence. throughout the sequence.
The first-differences form an arithmetic sequence
with first term  , so , so
 so so 
1. For  , , 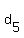 , , 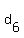 , you could just count by 2's to get , you could just count by 2's to get  ,' ,'  ,' ,'  , ,
and then find 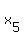 and and 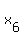 , ,
the 5th and 6th terms of the quadratic sequence,
maybe doing mental math while tabulating results, like this
 ---> --->  ---> ---> 
or you could apply the formula for 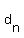 above to get above to get
 and and  . .
Either approach allows you to calculate 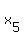 and and 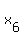 , ,
the 5th and 6th terms of the quadratic sequence.
 ---> ---> ---> ---> ---> --->
 ---> ---> ---> ---> ---> --->
2. Determining the nth term means finding a formula for 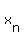 , ,
and that is where you will show your algebra skills.
You may want to find 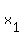 . .
You could keep working backwards to get 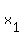 , ,
maybe without writing the calculations, just by tabulating the results of your mental math work,
 , ,
or maybe writing down calculations,
 , ,
 , ,
 , ,
 , ,
or you could calculate 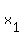 using formulas. using formulas.
Since the differences form an arithmetic sequence,
we know how to calculate the sum of all the  first-differences first-differences
that have to be added to get from 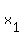 to term number to term number 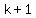


so  is an easy to calculate formula that you can use to relate is an easy to calculate formula that you can use to relate 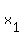 to a generic term number to a generic term number 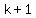 . .
So 



 . .
Now, for 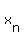 , we can use the simple formula , we can use the simple formula  <---> <--->



|
|
|