Question 1057143: The first 4 terms in a number sequence are 2, 5, 8, 11, ... ...
(a) Find the Nth term
(b) Explain if the term 105 is in the sequence
(c) By comparing to the number sequence, write down the general term for the sequence 4, 10, 16, 22, ...
Answer by ikleyn(52803)   (Show Source): (Show Source):
You can put this solution on YOUR website! .
The first 4 terms in a number sequence are 2, 5, 8, 11, ... ...
(a) Find the Nth term
(b) Explain if the term 105 is in the sequence
(c) By comparing to the number sequence, write down the general term for the sequence 4, 10, 16, 22, ...
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
The sequence 2, 5, 8, 11, ... is an arithmetic progression with the first term 2 and the common difference 3.
Is it clear to you? It should be clear if you just learned on arithmetic progressions.
The common term, the N-th term, therefore, is 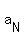 = 2 + 3*(N-1).
So, (a) is answered.
Let us check if the number 105 belongs to the sequence.
If 105 = 2 + 3*(N-1) for some integer N, then the answer is positive.
If such integer N does not exist, then the answer is negative.
OK. So, let 2 + 3*(N-1) = 105.
Then 3*(N-1) = 105 - 2 = 103.
Then (N-1) must be equal to = 2 + 3*(N-1).
So, (a) is answered.
Let us check if the number 105 belongs to the sequence.
If 105 = 2 + 3*(N-1) for some integer N, then the answer is positive.
If such integer N does not exist, then the answer is negative.
OK. So, let 2 + 3*(N-1) = 105.
Then 3*(N-1) = 105 - 2 = 103.
Then (N-1) must be equal to 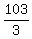 .
Is this number integer ? - NO.
Hence, there is no such an integer N that 2 + 3*(N-1) = 105.
It means that the number 105 does not belong to the sequence.
Answer for b). 105 is not the term of the sequence. .
Is this number integer ? - NO.
Hence, there is no such an integer N that 2 + 3*(N-1) = 105.
It means that the number 105 does not belong to the sequence.
Answer for b). 105 is not the term of the sequence.
Try to answer c) based on what you learned from my post.
If you want to know more about arithmetic progressions, read the lessons
- Arithmetic progressions
- The proofs of the formulas for arithmetic progressions
- Problems on arithmetic progressions
- Word problems on arithmetic progressions
in this site.
Also, you have this free of charge online textbook in ALGEBRA-II in this site
- ALGEBRA-II - YOUR ONLINE TEXTBOOK.
The referred lessons are the part of this online textbook under the topic
"Arithmetic progressions".
|
|
|