Question 862841: When an object falls, it gains speed. Thus the number of feet "d" the object has fallen is not linearly related to the number of seconds "t" spend falling. In fact, for objects falling near the surface of the Earth, with negligible resistance from the air, d=16t ^2 (16x t x t).
How many seconds would it take for a canon ball to reach the ground if it were dropped from the top of the Eiffel Tower, which is 984 feet tall? How many seconds would it take for the cannonball to reach the ground if it were dropped from a point that is halfway to the top?
Answer by ankor@dixie-net.com(22740)   (Show Source): (Show Source):
You can put this solution on YOUR website! When an object falls, it gains speed.
Thus the number of feet "d" the object has fallen is not linearly related to the number of seconds "t" spend falling.
In fact, for objects falling near the surface of the Earth, with negligible resistance from the air, d=16t ^2 (16x t x t).
:
How many seconds would it take for a canon ball to reach the ground if it were dropped from the top of the Eiffel Tower, which is 984 feet tall?
16x^2 = 984
x^2 = 984/16
x^2 = 61.5
x = 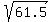
x = 7.8422 sec
:
How many seconds would it take for the cannonball to reach the ground if it were dropped from a point that is halfway to the top?
Do it the same way but now the equation is:
16x^2 = 492
|
|
|