Question 666507: Direction are complete the square.
x^2+2x=5
Am I suppose to set this to zero? When I do, I don't know what would make the sum of 2 and give me -5.
I get to x^2+2x-5=0
Answer by Leaf W.(135)   (Show Source): (Show Source):
You can put this solution on YOUR website! 
*
No, you are not supposed to set this equal to zero when you complete the square; that is for quadratic formula. It is in perfect starting format the way it is -- the coefficient of  (number it is multiplied; for example, the coefficient of x in 2x is 2) is 1, which is exactly what you want. Also, the two x terms (x^2 and 2x) are on the left of the equation, and the 5 is on the right, which is also correct. (number it is multiplied; for example, the coefficient of x in 2x is 2) is 1, which is exactly what you want. Also, the two x terms (x^2 and 2x) are on the left of the equation, and the 5 is on the right, which is also correct.
*
Divide the coefficient of the "x" term (in this case, the x term would be 2x, so its coefficient would be the number before the x, 2) in half. This would give you 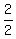 , or 1. , or 1.
*
Square this number:  = 1 = 1
*
Add the result to both sides of the equation: 
*
Simplify the right side of the equation: 
*
Factor the left side of the equation: 
*
Square root both sides. Remember that the right side could be either the positive or the negative square root: x + 1 = ±
*
Isolate the x by subtracting 1 from both sides: x = -1 ± 
*
Your final answer is x = -1 ±  . .
|
|
|