Question 1208432: when pipe is transported it is bundled into regular hexagons for stability during shipment. let n be the number of pieces of pipe on any side of the regular hexagon. write a rule for this situation. how many pieces of pipe are in a bundle when n = 12
the photo : imgur.com/a/3GF6R6G (IT IS NUMBER 2)
Found 2 solutions by ikleyn, greenestamps:
Answer by ikleyn(53560)   (Show Source): (Show Source):
You can put this solution on YOUR website! .
When pipe is transported it is bundled into regular hexagons for stability during shipment.
Let n be the number of pieces of pipe on any side of the regular hexagon.
Write a rule for this situation. How many pieces of pipe are in a bundle when n = 12 ?
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
A regular hexagon consists of 6 congruent equilateral triangles.
Let's consider one such a triangle as a bundle of pipes.
The number of pipes in one such a triangled bundle, with n pipes along each side
is the sum
1 + 2 + 3 + . . . + n =  . (1)
It is the sum of first n natural numbers, so this formula is very well known.
OK. But we have 6 such triangles in the hexagon. So, the first move is to multiply
the right side of (1) by 6 and to get 3n*(n+1).
But doing this way, we count n pipes twice along each common side of these triangles.
So, from 3n(n+1) we should subtract 6n to get 3n*(n+1) - 6n.
But this is not the end.
When we multiplied (1) by 6, we counted the central pipe 6 times.
Then we subtracted it 6 times.
Now to compensate everything, we should add 1 for the central pipe.
So, the final formula is
f(n) = 3n*(n+1) - 6n + 1, (2)
or, which is the same
f(n) = 3n^2 - 3n + 1. (3)
You may check, using your pictures for small n = 2, 3, 4, that this formula is correct.
f(12) = using formula (2) = 3*12*13 - 6*12 + 1 = 397. . (1)
It is the sum of first n natural numbers, so this formula is very well known.
OK. But we have 6 such triangles in the hexagon. So, the first move is to multiply
the right side of (1) by 6 and to get 3n*(n+1).
But doing this way, we count n pipes twice along each common side of these triangles.
So, from 3n(n+1) we should subtract 6n to get 3n*(n+1) - 6n.
But this is not the end.
When we multiplied (1) by 6, we counted the central pipe 6 times.
Then we subtracted it 6 times.
Now to compensate everything, we should add 1 for the central pipe.
So, the final formula is
f(n) = 3n*(n+1) - 6n + 1, (2)
or, which is the same
f(n) = 3n^2 - 3n + 1. (3)
You may check, using your pictures for small n = 2, 3, 4, that this formula is correct.
f(12) = using formula (2) = 3*12*13 - 6*12 + 1 = 397.
Solved, with explanations.
Thank you for asking.
Hope you will have fun reading this solution.
Answer by greenestamps(13292)   (Show Source): (Show Source):
You can put this solution on YOUR website!
Referring to the diagram on the referenced page will help understand the discussion below.
Let P(n) represent the number of pipes in the array when each side of the array is n units long.
When n=1, the "array" of pipes is a single pipe: P(1) = 1.
To make the array with n=2, you need to add 6(n-1) = 6(1) = 6 pipes to the array. P(2) = 1+6 = 7.
To make the array with n=3, you need to add 6(n-1) = 6(2) = 12 pipes to the array. P(3) = 7+12 = 19.
To make the array with n=4, you need to add 6(n-1) = 6(3) = 18 pipes to the array. P(4) = 19+18 = 37.
To make the array with n=5, you need to add 6(n-1) = 6(4) = 24 pipes to the array. P(5) = 37+24 = 61.
Now look at the sequence of values for P(n):
1, 7, 19, 37, 61, ...
You can find a polynomial expression for P(n) using the method of finite differences.
To use the method of of finite differences, you look at the differences between the terms of the sequence, then you look at the differences between those differences (the "second differences"), then you look at the differences between those second differences (the "third differences"), and so on, until you find a sequence of differences which is constant.
When you get a constant difference with the n-th differences, the polynomial will be of degree n.
Let's look at the sequence and its differences....
1 7 19 37 61 the sequence
6 12 18 24 the first differences
6 6 6 the second differences
The second differences are constant, so P(n) is a quadratic polynomial, of the form 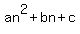 . .
One way to determine the polynomial is to form three equations in a, b, and c for any three of the known values of n. This will be easiest if you use n = 1, 2, and 3, since the numbers in the equations will be smaller.
Doing that is a good exercise in solving systems of polynomial equations; you might want to try to do that to see if you can get the result shown below.
If the polynomial is quadratic, I like to use a different method for determining the polynomial.
To do this, you need to know that the constant second difference is 2 times a, the leading coefficient of the polynomial. (If you have studied some calculus, this is due to the fact that the second derivative of a quadratic function is a constant.)
Since the constant difference is 6, the leading term of the quadratic polynomial is  . .
Use that leading term and the known values of the terms of the sequence to determine the linear part of the polynomial.
n P(n) 3n^2 difference P(n)-3n^2
----------------------------------------
1 1 3 -2
2 7 12 -5
3 19 27 -8
4 37 48 -11
The linear expression that produces that sequence of differences is 
So the quadratic polynomial that gives the number of pipes in an array when the number of pipes on each edge of the array is n is
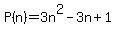
I assume that is the desired answer when the problem says to "write a rule for this situation".
When the number of pipes on each side of the array is 12, the number of pipes in the array is
ANSWER: 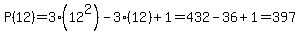
You can learn much more than you ever want to know about this sequence on the Online Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences, at the following URL:
oeis.org
-----------------------------------------------------------
NOTE: See the response from tutor @ikleyn for a very different and equally good solution, using less formal algebra and a lot of good logical analysis.
|
|
|