Question 147189: I need an explanation of why the Pythatgorean theorem can be used only for right triangles that an 8th grader can understand. What I know is that the Pythagorean Theorem is a special case of the Law of Cosines where the Cos(c) is equal to zero which only happens when c=90 degrees. But I don't think an 8th grader has had the law of cosines yet. I'd really appreciate some help with this. Thanks.
Found 2 solutions by mangopeeler07, Edwin McCravy:
Answer by mangopeeler07(462)   (Show Source): (Show Source):
You can put this solution on YOUR website! Here is why the Pythagorean Theorem can only be used to solve right triangles. The Pythagorean Theorem is  with a and b the length of the legs of the triangle and c as the hypotenuse, or the longest side. It has variations too, like with a and b the length of the legs of the triangle and c as the hypotenuse, or the longest side. It has variations too, like 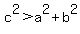 and and 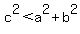 . These three are used to figure out, with given any angles, whether a triangle is right, obtuse or acute (respectively) by plugging in the lengths given. If . These three are used to figure out, with given any angles, whether a triangle is right, obtuse or acute (respectively) by plugging in the lengths given. If 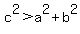 or or 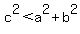 holds true, than the triangle is obtuse or acute. But if holds true, than the triangle is obtuse or acute. But if  holds true, than the triangle is right, and it has to be right. You are probably more familiar with this version: holds true, than the triangle is right, and it has to be right. You are probably more familiar with this version:  . It is only true for right triangles, because of the unique relationship among the three side lengths, which never holds true for any other type of triangle. That is why this variation of it (with the = sign) can only be used for right triangles and right triangles only. Right triangles are the only triangles that make this . It is only true for right triangles, because of the unique relationship among the three side lengths, which never holds true for any other type of triangle. That is why this variation of it (with the = sign) can only be used for right triangles and right triangles only. Right triangles are the only triangles that make this  true. true.
Answer by Edwin McCravy(20055)   (Show Source): (Show Source):
|
|
|