Question 1205804: The weather forecast in the cities of a province is modelled using a simple model that determines whether it will rain, be cloudy or sunny, only by
taking into account the previous day's weather. In this case, the model tells us that:
- a sunny day has a 70% chance that it will still be sunny the following day
- a rainy day has a 70% chance that it will still be rainy the next day
- sunny days and rainy days cannot be consecutive
- the probability that a cloudy day remains cloudy coincides with the normalised distance from the city to a reference centre. This probability is
we denote byr
- finally, the probability that a cloudy day becomes rainy or sunny is the same.
1. Write the transition matrix A (as a function of the parameter r)
I did the transition matrix A. Please see below:
rainy [7/10, -1/2r + 1/2, 3/10]
A= cloudy[0, r, 0]
sunny [3/10, -1/2 + 1/2, 7/10]
According to the exercise the sum of the elements in each column must be 1.
I can't understand the next exercise, can somebody help me?
2. We know that in a city today is a cloudy day and that the forecast for tomorrow is: 17 % rainy, 66 % cloudy and 17 % sunny. What is the normalised distance from this city to the reference point?
i don't underestand how to do it.
Answer by ikleyn(52754)   (Show Source): (Show Source):
You can put this solution on YOUR website! .
First, looking into your post, I see that the matrix A is written INCORRECLY:
in its row "sunny" you missed "r" in the second element; You must fix it.
Next, you should understand how the matrix A works and for what purpose it is intended.
Matrix A is an operator to predict the weather (the different probabilities for the weather) for tomorrow
based on the weather today.
It works this way
vector "wheather tomorrow" = A * vector "wheather today". (1)
As I read your post and your question #2, you are given
vector "wheather tomorrow" =  = = 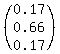 ,
vector "wheather today" = ,
vector "wheather today" =  = = 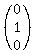 .
Based on this, they want you find the value of "r" in matrix A from equation (1).
If you write this equation (1) is scalar form, you will get three scalar equations
(-1/2r + 1/2)*1 = 0.17 (a)
r*1 = 0.66 (b)
(-1/2r + 1/2)*1 = 0.17 (c)
Then from equation (b) you find r = 0.66, and (FORTUNATELY !) this value of "r"
satisfies also equations (a) and (c).
Thus you find "r" this way, AND, by definition, you find the necessary value
of the normalized distance from the city to a reference center,
because, by the definition, this quantity is PRECISELY the value of "r". .
Based on this, they want you find the value of "r" in matrix A from equation (1).
If you write this equation (1) is scalar form, you will get three scalar equations
(-1/2r + 1/2)*1 = 0.17 (a)
r*1 = 0.66 (b)
(-1/2r + 1/2)*1 = 0.17 (c)
Then from equation (b) you find r = 0.66, and (FORTUNATELY !) this value of "r"
satisfies also equations (a) and (c).
Thus you find "r" this way, AND, by definition, you find the necessary value
of the normalized distance from the city to a reference center,
because, by the definition, this quantity is PRECISELY the value of "r".
Thus, I explained you the meaning of the problem, solved it and answered your question.
|
|
|