Question 1203104: Find the probability that in 200 tosses of a fair six-sided die, a five will be obtained at least 40 times
Answer by ikleyn(52781)   (Show Source): (Show Source):
You can put this solution on YOUR website! .
Find the probability that in 200 tosses of a fair six-sided die,
a five will be obtained at least 40 times
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
The original problem is on Binomial distribution
n = 200 total trials; p = 1/6 is the probability of an individual success
(obtaining a five in each individual toss);
k >= 40 is the number of successful trials.
Since the number of trials is great (200), it is recommended to use
the normal distribution as an approximation.
The mean of this normal distribution is m = n*p = 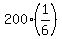 = =  = 33.333333 (rounded);
the standard deviation is
SD = = 33.333333 (rounded);
the standard deviation is
SD = 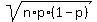 = = 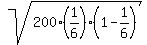 = 5.2704628 (rounded).
Now you can use your regular calculator TI-83 or TI-84. You get then
z1 z2 mean SD <<<---=== formatting pattern
p = normalcdf( 39.5, 9999, 33.333333, 5.2704628) = 0.121 (rounded). ANSWER
The number 39.5 comes with the continuity correction. = 5.2704628 (rounded).
Now you can use your regular calculator TI-83 or TI-84. You get then
z1 z2 mean SD <<<---=== formatting pattern
p = normalcdf( 39.5, 9999, 33.333333, 5.2704628) = 0.121 (rounded). ANSWER
The number 39.5 comes with the continuity correction.
Solved.
----------------------
About approximation of the binomial distribution by normal distribution and continuity correction factor
see your textbook and/or these Internet sources
https://www.statology.org/normal-approximation
https://www.statisticshowto.com/probability-and-statistics/binomial-theorem/normal-approximation-to-the-binomial/
https://online.stat.psu.edu/stat414/lesson/28/28.1
https://stats.libretexts.org/Courses/Las_Positas_College/Math_40%3A_Statistics_and_Probability/06%3A_Continuous_Random_Variables_and_the_Normal_Distribution/6.04%3A_Normal_Approximation_to_the_Binomial_Distribution
For calculations, you may use your calculator TI-83 or TI-84 (function normcdf)
or online calculator https://onlinestatbook.com/2/calculators/normal_dist.html
If you are a beginner student in learning probability distribution, I advise you to start learning
this kind of computations using the online calculator, to which I referred above.
It provides a graphical support, so at each step you do understand what you are doing.
In addition, this graphical support prevents you from making mistakes.
When you learm enough this kind of computations, you can switch to your regular calculator,
but even then you may use the online calculator for checking purposes.
|
|
|