.
A drawer contains 5 red socks and three black socks. A sock is taken out at random and not replaced.
A second sock is then taken out. Draw a tree diagram and calculate the probability
that either pair of red socks or a pair of black socks is chosen.
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
We want to calculate the probability having a pair of red socks or a pair of black socks
P = P(RR or BB).
First of all, it is clear that these events RR or BB are disjoint: they have empty intersection,
which means that they can not happen simultaneously.
Therefore, P(RR or BB) = P(RR) + P(BB) : the probability of this combined event is the sum
of probabilities of particular events.
So, we can calculate two probabilities P(RR) and P(BB) separately and then add them.
Let's calculate P(RR).
Originally, we have 5 red socks among 5+3 = 8 socs. So the probability to draw 1st sock red is 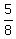 .
After that, we have 4 red socks and 8-1=7 socks remaining. So, the probability to draw 2nd sock red is
.
After that, we have 4 red socks and 8-1=7 socks remaining. So, the probability to draw 2nd sock red is  .
The probability to have both socks read after two drawing is the product
.
The probability to have both socks read after two drawing is the product  =
=  .
Let's calculate P(BB). The logic is very similar.
Originally, we have 3 black socks among 5+3 = 8 socs. So the probability to draw 1st sock black is
.
Let's calculate P(BB). The logic is very similar.
Originally, we have 3 black socks among 5+3 = 8 socs. So the probability to draw 1st sock black is 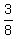 .
After that, we have 2 black socks and 3-1 = 2 socks remaining. So, the probability to draw 2nd sock black is
.
After that, we have 2 black socks and 3-1 = 2 socks remaining. So, the probability to draw 2nd sock black is  .
The probability to have both socks black after two drawing is the product
.
The probability to have both socks black after two drawing is the product  =
= 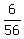 .
Finally, we shoud add the two found probabilities. We get then
P(RR or BB) =
.
Finally, we shoud add the two found probabilities. We get then
P(RR or BB) =  +
+ 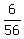 =
=  =
= 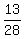 . ANSWER
. ANSWER
Solved.
----------------------
There are other ways to solve this problem, but this way is the simplest:
it requires a minimum knowledge.