Question 1195524: 3. The frequency distribution of the weights of 60 pieces of luggage, recorded to the nearest kilogram, belonging to the passengers on a flight from Manila to Cebu is shown below:
Weight (kilograms) Pieces
7-9 2
10-12 8
13-15 10
16-18 17
19-21 23
22-24 3
Calculate the range and the mean.
Answer by ikleyn(52781)   (Show Source): (Show Source):
You can put this solution on YOUR website! .
The frequency distribution of the weights of 60 pieces of luggage, recorded to the nearest kilogram, belonging to the passengers on a flight from Manila to Cebu is shown below:
Weight (kilograms) Pieces
7-9 2
10-12 8
13-15 10
16-18 17
19-21 23
22-24 3
Calculate the range and the mean.
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
To calculate the range, we should determine its lower boundary and its upper boundary.
To calculate the lower boundary, in the column "Weight" take smallest values,
multiply each such value by the factor "Pieces" and add all such products over all
the rows of the table
lower boundary = 7*2 + 10*8 + 13*10 + 16*17 + 19*23 + 22*3. Use your calculator.
To calculate the upper boundary, in the column "Weight" take greatest values,
multiply each such value by the factor "Pieces" and add all such products over all
the rows of the table
upper boundary = 9*2 + 12*8 + 15*10 + 18*17 + 21*23 + 24*3. Use your calculator.
Thus the range is this interval [lower boundary, upper boundary].
+---------------------------------------------------------+
| Regarding the mean, the problem does not determine |
| WHICH mean it wants to compute, UNFORTUNATELY, |
| which is a BIG FAULT for a Math problem. |
+---------------------------------------------------------+
In this problem, there are TWO meaningful conceptions of the "mean".
One conception of the mean is "total mean weight".
It is the arithmetic mean of the lower and upper range values
mean as the "mean total weight" = 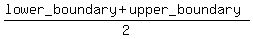 .
Another conception of the mean is "mean weight per single item".
It is the mean total weight divided by the total number of items/(pieces)
mean as the "mean weight per single item" = .
Another conception of the mean is "mean weight per single item".
It is the mean total weight divided by the total number of items/(pieces)
mean as the "mean weight per single item" = 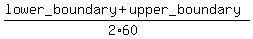 . .
At this point, I complete my explanations.
|
|
|