Question 879623: When the parabola y=x^2-a(x+1)+3 intersects the x-axis at one point then a= ? Or ?
Answer by josgarithmetic(39617)   (Show Source): (Show Source):
You can put this solution on YOUR website! 
 , you should c.... you can use the general solution to a quadratic equation. Watch for defined variables in the present equation and not confuse them with the instructionally typical variables. , you should c.... you can use the general solution to a quadratic equation. Watch for defined variables in the present equation and not confuse them with the instructionally typical variables.

Fitting the parts into the formula places,
roots are 

Because you want x to be only a single value as a root, you want the discriminant,  . FACTORABLE: . FACTORABLE:

-
-
---------------------
a=2 OR a=-6
---------------------
CONCEPTUAL DISCUSSION
"y intersects the x axis", means y=0, so that the solutions for x are the "roots" of y.
When we solve this for the equation that you were given,  , the application of the general solution of a quadratic formula gives us that x is this formula or expression: , the application of the general solution of a quadratic formula gives us that x is this formula or expression:
 . .
This or these are the x values for which y crosses or touches the x-axis.
If you specify that y has exactly ONE root, then y intersects the x-axis at ONE point only. This can occur only for  , from the solution of x. The expression , from the solution of x. The expression 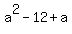 from your solutions of x is the discriminant. from your solutions of x is the discriminant.
The typical model for instruction in discussing a quadratic formula is much expressed as  , but typically the lower-case coefficients and constant are used. The discriminant for this general quadratic equation would be , but typically the lower-case coefficients and constant are used. The discriminant for this general quadratic equation would be 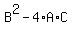 . In keeping with the known and derivable generality about roots of the equation, the discriminant is zero if there is only one root (or only one x-intercept.) . In keeping with the known and derivable generality about roots of the equation, the discriminant is zero if there is only one root (or only one x-intercept.)
|
|
|