Question 1092443: Determine the stopping distances for a car with an initial speed of 93 km/h and human reaction time of 3.0 s for the following accelerations.
(a) a = -4.0 m/s^2
(b) a = -8.0 m/s^2
Answer by KMST(5328)   (Show Source): (Show Source):
You can put this solution on YOUR website! IN IDEAS:
   . .
At that speed, during the 3.0 seconds allowed for reaction time,
the vehicle would cover a distance of
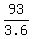  . .
The graph of speed (in m/s) as a function of time (in seconds)
for the first case (a=-4.0m/s^2) is
 , ,
and the stopping distance is the area under the curve.
To go from initial speedspeed to 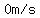
at   it would take it would take 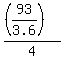   . .
During that time, speed would be changing linearly,
with an average speed of 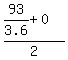   , ,
and covering a distance of
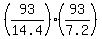  . .
The total stopping distance would be about

As the acceleration and initial speed were given with two significant digits,
it would be proper to report the stopping distance as
 . .
With an acceleration of -8.0 m/s^2 (twice as large in magnitude),
the stopping time would be 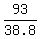  . .
During that time, with the same average speed calculated above,
the vehicle would cover a distance of
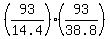  . .
That results in a total stooping distance of
 to be reported as to be reported as  . .
IN FORMULAS:
With d=distance, v=velocity, a=acceleration, and t=time, in SI units (only meters and seconds allowed),
 for uniform linear motion (constant speed for the 3.0 seconds of reaction time), and for uniform linear motion (constant speed for the 3.0 seconds of reaction time), and
 for uniformly accelerated linear motion (the braking part). for uniformly accelerated linear motion (the braking part).
|
|
|