Question 1083096: Find trigonometric functions of angle α in a rightangled triangle with hypotenuse = 13cm and leg (catheti) = 12 cm
Found 2 solutions by Alan3354, KMST:
Answer by Alan3354(69443)   (Show Source): (Show Source):
You can put this solution on YOUR website! It's a right triangle with sides a = 5, b = 12 & c = 13.
------
Angle C is the right angle = 90 degs.
sin(C) = 1
cos(C) = 0
----------
Angle A is the smallest angle opposite side a.
sin(A) = 5/13
cos(A) = 12/13
---------
Angle B is the angle opposite side b.
sin(B) = 12/13
cos(B) = 5/13
======================
For all angles,
tan = sin/cos
cot = 1/tan
sec = 1/cos
csc = 1/sin
Answer by KMST(5328)   (Show Source): (Show Source):
You can put this solution on YOUR website! Without a picture with side lengths and angle  labeled, labeled,
or some other way to figure out if angle  is opposite or adjacent to the 12-cm leg, is opposite or adjacent to the 12-cm leg,
I cannot give you the trigonometric functions of angle  , ,
but I can draw your triangle as triangle ABC, with right angle at A,
and give you the trigonometric functions of acute angles B and C.
You will have o figure out which one is  . .
 B is the angle adjacent to the 12-cm leg, C is opposite the 12-cm leg. B is the angle adjacent to the 12-cm leg, C is opposite the 12-cm leg.
You need the length,  , of leg AC. , of leg AC.
For that you use the Pythagorean theorem.
Applied to this triangle, it says

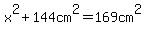
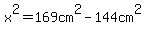


With that length you can calculate values of all trigonometric functions for the acute angles.
Then you use the definitions for trigonometric ratios for a right triangle
 , and , and  . .
You may know tangent defined as
 , ,
or you may have learned it as
 . .
If you are expected to calculate cotangent, secant and cosecant, you would use
 , ,  and and  . .
As a tutor, I would prefer to see you figure it out from this point on,
but I will give you the answers because
you are not here to be persuaded to do the work,
and the website tells me that tutors "MUST SHOW ALL WORK."

|
|
|